Cut
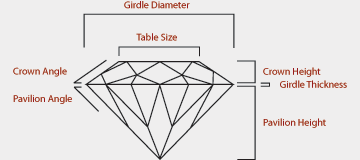
When you think of the cut, you probably think of the shape of the diamond. You are partially correct. While cut does refer to shape, it also refers to the proportions of how the diamond is cut.
Diamonds are cut into many different shapes, reflecting not only popular taste but the proportions and quality of the rough diamond. The most popular shapes include Round, Oval, Square, Princess, Emerald, Baquette, and Marquise. Many specialty shapes are also available.
A diamond's overall proportions, as well as the size and placement of its many reflective surfaces or facets, also play a large part in its cut. The consistency and balance of these can greatly affect how the stone captures light and reflects it back to the eye.

Color
With the exception of some fancy colored diamonds, the most valuable diamonds are those with the least color. The color scale for transparent diamonds runs from D-F (colorless), G-J (near colorless), K-L (faint yellow), to Z (light yellow). Completely colorless diamonds are rare.
When diamonds are formed with traces of other minerals, rare and beautiful colors can result. These fancy colors range from blue to brilliant yellow to red, brown, pale green, pink, and violet. Because of their rarity, colored diamonds are highly desirable and may be quite valuable.
|
D
|
E
|
F
|
G
|
H
|
I
|
J
|
K
|
L
|
M
|
N
|
O
|
P
|
Q
|
R
|
S
|
T
|
U
|
V
|
W
|
X
|
Y
|
Z
|
Z+
|
| Colorless | Near Colorless | Faint Yellow | Very Light Yellow | Light Yellow | Fancy | ||||||||||||||||||

Clarity
A diamond's clarity is measured by the existence, or absence, of visible flaws. Tiny surface blemishes or internal inclusions - even those seen only under magnification with a jeweler's loupe - can alter the brilliance of the diamond and affect its value. Clarity levels begin with Flawless (F & IF) and move down to Very Very Slight (VVS1 & 2), Very Slight (VS1 & 2), Slightly Included (SI1 & 2), and Included (I1, 2 & 3).
| FL, IF Diamonds | Flawless: No internal or external flaws Internally Flawless: No internal flaws |
| VVS1, VVS2 Diamonds | Very, Very Slightly Included: Very difficult to see inclusions under 10% magnification. |
| VS1, VS2 Diamonds | Very Slightly included: Inclusions are not typically visible to the unaided eye, |
| SI1, SI2 Diamonds | Slightly included: Inclusions are visible under 10× magnification and may be visible to the unaided eye. |
| I1, I2, I3 Diamonds | Included: Inclusions are visible with the unaided eye. |

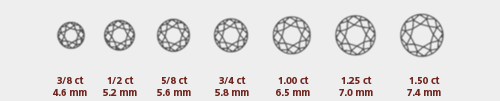
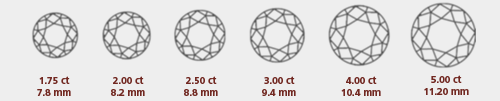
Carat
The size of a diamond is measured by weight. One carat, the traditional unit of measure for diamonds, is equal to approximately 0.2 grams. You may also hear the weight of a diamond referred to in points. A point is equal to 1/100 of a carat; Therefore, a 75-point diamond equals 0.75 carat. Diamonds of equal weight may appear slightly different in size, depending on their depth and proportions. Because they are quite rare, larger diamonds of gem quality are much more valuable.